Trauma affects everyone differently. Learn more about acute stress disorder symptoms, causes and different treatment options and discover how to get the help you need.
Acute stress disorder is amental health conditionthat can develop in response to trauma experienced directly or indirectly. While the symptoms of this condition can interfere with daily life and well-being, treatment is available. With professional care, many people find relief from their symptoms and proceed to live healthy, fulfilling lives.
What Is Acute Stress Disorder?
The acute stress disorder definition refers to the cluster of symptoms that may result in response to one’s exposure to trauma. As we know, trauma can trigger a host of both physical and psychological effects that can be challenging.
Acute stress disorder criteria include symptoms related to avoidance, arousal, dissociation, numbness, and heightened distress. While these symptoms may cause significant impairment, they do not exceed longer than a month after the traumatic incident.
Acute Stress Disorder vs. PTSD
Acute stress disorder is often confused withpost-traumatic stress disorder(PTSD). Although they have many similarities, sorting out thedifferencesbetween acute stress disorder vs. PTSD comes down to specific symptoms and timelines. Acute stress disorder occurs within 30 days of a traumatic event, and symptoms last anywhere from three days to four weeks. However, symptoms cannot last for longer than this period; if they do, the individual is given a PTSD diagnosis.
[elementor-template id="4848"]PTSDdevelops at least one month after a traumatic incident. Delayed onset can occur, and the first symptoms may not emerge for three to six months. While symptoms must last for at least a month for a diagnosis to be made, they may persist for several months or years.
Signs and Symptoms of Acute Stress Disorder
There are several acute stress disorder symptoms. These symptoms can be broken up into five different categories: avoidance, arousal, dissociative, numbness and distress symptoms.
- Avoidance Symptoms:In response to the trauma, people will avoid distressing stimuli that cause them to re-experience the event. These stimuli may include people, places, activities, objects, feelings or thoughts. Avoidance can result in additional problems, especially if it causes a person to avoid necessary work or family obligations.
- Arousal Symptoms:Heightened arousal can include increased anxiety, difficulty concentrating, restlessness, sleep problems, irritability and hypervigilance. Many people experiencing these symptoms find it challenging to enjoy the present moment, as they feel a constant sense of being “on guard” and aware of their surroundings. They may struggle with concentration and feel more irritable and agitated throughout the day.
- Dissociative Symptoms:Dissociative symptoms may involve numbness, depersonalization (when thoughts don’t feel real), derealization (when the environment doesn’t seem real) anddissociative amnesia(unable to remember certain parts of the trauma). Individuals may be aware or unaware of the nature of these symptoms.
- Numbness:Numbness refers to feeling detachment or emotionally “blank” after a trauma. Many people describe feeling a sense of nothingness when recalling the event.
- Distress:Distress refers to the discomfort or disruption of certain tasks (like work, school or home responsibilities) in response to the trauma. After the incident, people may feel overwhelmed, anxious, depressed or even suicidal, which makes it challenging to fulfill necessary obligations.

Diagnosing Acute Stress Disorder
Mental health professionals provide an acute stress disorder diagnosis when individuals experience exposure to trauma and have the presence of at least nine symptoms from any of the five categories (avoidance, arousal, dissociative, numbness, distress). Symptoms also must last for no longer than one month for this diagnosis to be made.
Causes of Acute Stress Disorder
While it is impossible to determine who will or will not develop acute stress disorder, trauma is the defining, underlying factor that exists in all cases. Typical examples of trauma include:
- Threatened or actual physical violence
- Sexual assault
- Exposure to war or serious crime
- Kidnapping or torture
- Severe accidents
- Natural disasters
- Witnessing medical catastrophes in another person (i.e., suicide, overdoses or heart attacks)
The combination of any of these incidents can result in significant distress, which can lead to the development of acute stress disorder.
Risk Factors for Acute Stress Disorder
The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5) lists the following acute stress disorder risk factors:
- Temperamental:Individuals with a history of previous mental disorders (i.e.,depression,anxiety) may have a higher likelihood of developing acute stress disorder. Furthermore, people with more avoidant coping styles and exaggerated responses related to hopelessness, shame or future chances for harm also be more likely to develop acute stress disorder.
- Genetic and Physiological:Research shows that women are more likely to develop acute stress disorder than men. Moreover, elevated reactivity (tendency to a heightened startle response) is also a risk factor.
- Environmental:An individual must be exposed to a traumatic event to develop acute stress disorder.

Statistics on Acute Stress Disorder
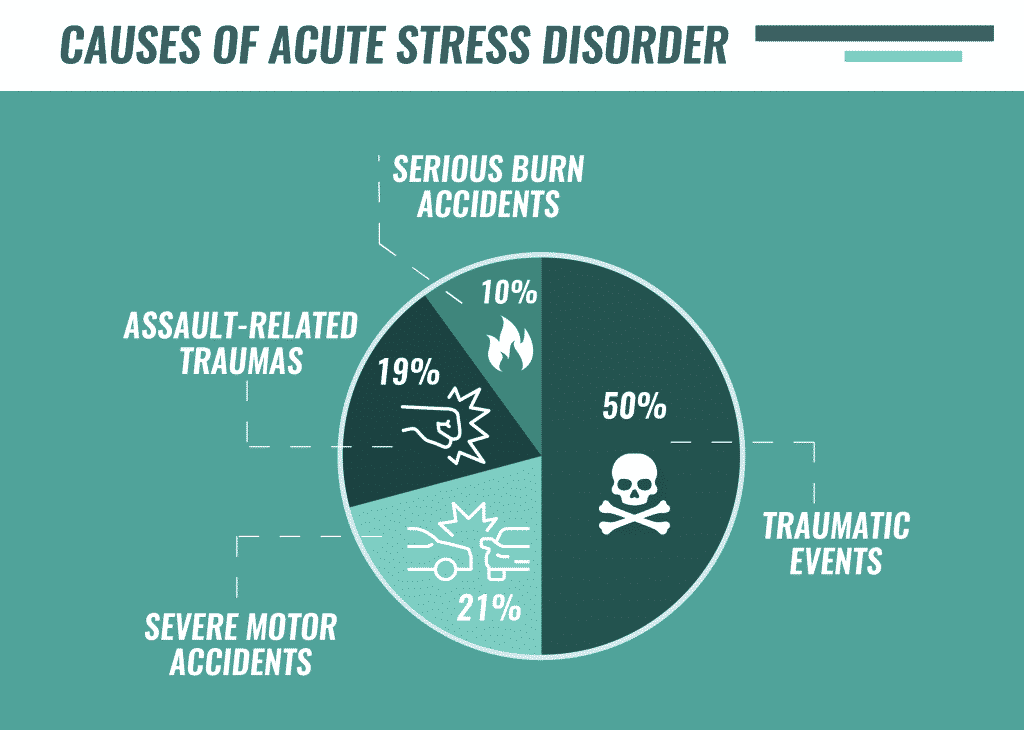
The DSM-5 also highlights the followingacute stress disorder statistics:
- Up to 20–50 percent of people experiencing interpersonal traumatic events (assault, rape, witnessing death) develop acute stress disorder
- Between 13–21 percent of individuals involved in severe motor vehicle accidents develop acute stress disorder
- 10 percent of individuals involved in serious burn accidents or injuries develop acute distress disorder
- 19 percent of individuals involved in assault-related traumas develop acute stress disorder
That said, statistics can be challenging to verify, especially because many individuals who struggle with acute stress disorder symptoms do not receive the treatment or help they need. Therefore, it is difficult to accurately assess the prevalence of this mental disorder.
Acute Stress Disorder and Co-Occurring Conditions
There is a strong relationship between acute stress and other mental health conditions, includingsubstance use disorders. Many people turn to mood-altering substances to self-medicate the symptoms associated with acute stress disorder. Drugs and alcohol can create a sense of short-term relief that many find difficult to resist. Research shows that nearly60 percent of adolescentswith PTSD develop substance use problems. Furthermore, between 25 and 75 percent of adults use substances after a traumatic incident.
Treatment for Acute Stress Disorder
Acute stress disorder treatment optionstypically include a combination of pharmacotherapy and psychotherapy. Pharmacotherapy may involve antidepressants or anticonvulsants that can help with depressive, intrusive, avoidance or dissociative symptoms. Medication for acute pain management in cases where trauma involved a physical injury can also be helpful.
Psychotherapy treatment is typically comprised oftrauma-focused cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) to provide individuals with support and normalization for their symptoms and experiences. During therapy, clients:
- Are exposed to triggers to reduce heightened arousal related to the event
- Undergo cognitive processing that helps them reframe negative messages associated with the trauma
- Examine interpersonal issues to help support individuals struggling with family or marital distress as a result of the trauma
At The Recovery Village, we provide support for PTSD and acute stress disorders that co-occur with substance use disorders. If you or a loved one lives with these conditions, we are here to help.Reach outfor support today.
